计算 Jaccard 相似性度量的 gremlin 语法
gremlin syntax to calculate Jaccard similarity metric
我对计算图中所有不直接连接的顶点对的 Jaccard 相似度度量很感兴趣。 Jaccard 度量定义为两个顶点的相邻顶点的交集的范数除以相同集合的并集的范数。
%5Cmid&space;x%5Cneq&space;y)
=&space;%5Cfrac%7B%5Cleft&space;|N(x)%5Ccap&space;N(y)&space;%5Cright&space;|%7D%7B%5Cleft&space;|N(x)%5Ccup&space;N(y)&space;%5Cright&space;|%7D)
哪里
=set~of~all~neighbors~of~vertex~x)
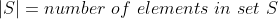
到目前为止,我已经能够得到所有未直接连接的节点对(只对这种情况感兴趣,用于 link 预测,如果直接 link 已经存在,那么我不需要计算 Jaccard 度量)使得对于一对 (x, y) 其中 x 不等于 y:
g.V().as('v1').V().where(neq('v1')).as('v2').filter(__.not(inE().where(outV().as('v1'))))
除此之外,我还包括了标记为 v1out 和 v2out 的每对成员的邻居:
g.V().as('v1').out().as('v1out').V().where(neq('v1')).as('v2').filter(__.not(inE().where(outV().as('v1')))).out().as('v2out')
从这里我将如何执行集合操作来获取两个相邻集合的交集和并集中的元素数?之后,我相信我可以附加数学步骤(目前使用 TinkerPop 3.4.0)来计算 Jaccard 相似率,然后选择步骤在值大于阈值时添加边。如果一个完全不同的方法比上面的部分解决方案有好处,我很乐意采用它并最终使它工作。
让我们一步一步来:
查找顶点对并收集它们各自的邻居:
g.V().match(
__.as('v1').out().dedup().fold().as('v1n'),
__.as('v1').V().as('v2'),
__.as('v2').out().dedup().fold().as('v2n')).
where('v1', neq('v2'))
确保 v1 不是 v2 的邻居,反之亦然:
g.V().match(
__.as('v1').out().dedup().fold().as('v1n'),
__.as('v1').V().as('v2'),
__.as('v2').out().dedup().fold().as('v2n')).
where('v1', neq('v2').and(without('v2n'))).
where('v2', without('v1n'))
接下来,计算相交邻居数和邻居总数:
g.V().match(
__.as('v1').out().dedup().fold().as('v1n'),
__.as('v1').V().as('v2'),
__.as('v2').out().dedup().fold().as('v2n')).
where('v1', neq('v2').and(without('v2n'))).
where('v2', without('v1n')).as('m').
project('v1','v2','i','u').
by(select('v1')).
by(select('v2')).
by(select('v1n').as('n').
select('m').
select('v2n').unfold().
where(within('n')).
count()).
by(union(select('v1n'),
select('v2n')).unfold().
dedup().count())
最后,通过将 i 除以 u 来计算 Jaccard 相似度(还要确保过滤掉没有邻居的顶点以防止除以 0):
g.V().match(
__.as('v1').out().dedup().fold().as('v1n'),
__.as('v1').V().as('v2'),
__.as('v2').out().dedup().fold().as('v2n')).
where('v1', neq('v2').and(without('v2n'))).
where('v2', without('v1n')).as('m').
project('v1','v2','i','u').
by(select('v1')).
by(select('v2')).
by(select('v1n').as('n').
select('m').
select('v2n').unfold().
where(within('n')).
count()).
by(union(select('v1n'),
select('v2n')).unfold().
dedup().count()).
filter(select('u').is(gt(0))).
project('v1','v2','j').
by(select('v1')).
by(select('v2')).
by(math('i/u'))
最后一件事:由于比较顶点v1和v2与比较v2和v1相同,查询只需要考虑一种情况。一种方法是确保 v1 的 id 小于 v2 的 id:
g.V().match(
__.as('v1').out().dedup().fold().as('v1n'),
__.as('v1').V().as('v2'),
__.as('v2').out().dedup().fold().as('v2n')).
where('v1', lt('v2')).
by(id).
where('v1', without('v2n')).
where('v2', without('v1n')).as('m').
project('v1','v2','i','u').
by(select('v1')).
by(select('v2')).
by(select('v1n').as('n').
select('m').
select('v2n').unfold().
where(within('n')).
count()).
by(union(select('v1n'),
select('v2n')).unfold().
dedup().count()).
filter(select('u').is(gt(0))).
project('v1','v2','j').
by(select('v1')).
by(select('v2')).
by(math('i/u'))
在 the modern toy graph 上执行此遍历会产生以下结果:
gremlin> g = TinkerFactory.createModern().traversal()
==>graphtraversalsource[tinkergraph[vertices:6 edges:6], standard]
gremlin> g.V().match(
......1> __.as('v1').out().dedup().fold().as('v1n'),
......2> __.as('v1').V().as('v2'),
......3> __.as('v2').out().dedup().fold().as('v2n')).
......4> where('v1', lt('v2')).
......5> by(id).
......6> where('v1', without('v2n')).
......7> where('v2', without('v1n')).as('m').
......8> project('v1','v2','i','u').
......9> by(select('v1')).
.....10> by(select('v2')).
.....11> by(select('v1n').as('n').
.....12> select('m').
.....13> select('v2n').unfold().
.....14> where(within('n')).
.....15> count()).
.....16> by(union(select('v1n'),
.....17> select('v2n')).unfold().
.....18> dedup().count()).
.....19> filter(select('u').is(gt(0))).
.....20> project('v1','v2','j').
.....21> by(select('v1')).
.....22> by(select('v2')).
.....23> by(math('i/u'))
==>[v1:v[1],v2:v[5],j:0.0]
==>[v1:v[1],v2:v[6],j:0.3333333333333333]
==>[v1:v[2],v2:v[4],j:0.0]
==>[v1:v[2],v2:v[6],j:0.0]
==>[v1:v[4],v2:v[6],j:0.5]
==>[v1:v[5],v2:v[6],j:0.0]
我对计算图中所有不直接连接的顶点对的 Jaccard 相似度度量很感兴趣。 Jaccard 度量定义为两个顶点的相邻顶点的交集的范数除以相同集合的并集的范数。
哪里
到目前为止,我已经能够得到所有未直接连接的节点对(只对这种情况感兴趣,用于 link 预测,如果直接 link 已经存在,那么我不需要计算 Jaccard 度量)使得对于一对 (x, y) 其中 x 不等于 y:
g.V().as('v1').V().where(neq('v1')).as('v2').filter(__.not(inE().where(outV().as('v1'))))
除此之外,我还包括了标记为 v1out 和 v2out 的每对成员的邻居:
g.V().as('v1').out().as('v1out').V().where(neq('v1')).as('v2').filter(__.not(inE().where(outV().as('v1')))).out().as('v2out')
从这里我将如何执行集合操作来获取两个相邻集合的交集和并集中的元素数?之后,我相信我可以附加数学步骤(目前使用 TinkerPop 3.4.0)来计算 Jaccard 相似率,然后选择步骤在值大于阈值时添加边。如果一个完全不同的方法比上面的部分解决方案有好处,我很乐意采用它并最终使它工作。
让我们一步一步来:
查找顶点对并收集它们各自的邻居:
g.V().match(
__.as('v1').out().dedup().fold().as('v1n'),
__.as('v1').V().as('v2'),
__.as('v2').out().dedup().fold().as('v2n')).
where('v1', neq('v2'))
确保 v1 不是 v2 的邻居,反之亦然:
g.V().match(
__.as('v1').out().dedup().fold().as('v1n'),
__.as('v1').V().as('v2'),
__.as('v2').out().dedup().fold().as('v2n')).
where('v1', neq('v2').and(without('v2n'))).
where('v2', without('v1n'))
接下来,计算相交邻居数和邻居总数:
g.V().match(
__.as('v1').out().dedup().fold().as('v1n'),
__.as('v1').V().as('v2'),
__.as('v2').out().dedup().fold().as('v2n')).
where('v1', neq('v2').and(without('v2n'))).
where('v2', without('v1n')).as('m').
project('v1','v2','i','u').
by(select('v1')).
by(select('v2')).
by(select('v1n').as('n').
select('m').
select('v2n').unfold().
where(within('n')).
count()).
by(union(select('v1n'),
select('v2n')).unfold().
dedup().count())
最后,通过将 i 除以 u 来计算 Jaccard 相似度(还要确保过滤掉没有邻居的顶点以防止除以 0):
g.V().match(
__.as('v1').out().dedup().fold().as('v1n'),
__.as('v1').V().as('v2'),
__.as('v2').out().dedup().fold().as('v2n')).
where('v1', neq('v2').and(without('v2n'))).
where('v2', without('v1n')).as('m').
project('v1','v2','i','u').
by(select('v1')).
by(select('v2')).
by(select('v1n').as('n').
select('m').
select('v2n').unfold().
where(within('n')).
count()).
by(union(select('v1n'),
select('v2n')).unfold().
dedup().count()).
filter(select('u').is(gt(0))).
project('v1','v2','j').
by(select('v1')).
by(select('v2')).
by(math('i/u'))
最后一件事:由于比较顶点v1和v2与比较v2和v1相同,查询只需要考虑一种情况。一种方法是确保 v1 的 id 小于 v2 的 id:
g.V().match(
__.as('v1').out().dedup().fold().as('v1n'),
__.as('v1').V().as('v2'),
__.as('v2').out().dedup().fold().as('v2n')).
where('v1', lt('v2')).
by(id).
where('v1', without('v2n')).
where('v2', without('v1n')).as('m').
project('v1','v2','i','u').
by(select('v1')).
by(select('v2')).
by(select('v1n').as('n').
select('m').
select('v2n').unfold().
where(within('n')).
count()).
by(union(select('v1n'),
select('v2n')).unfold().
dedup().count()).
filter(select('u').is(gt(0))).
project('v1','v2','j').
by(select('v1')).
by(select('v2')).
by(math('i/u'))
在 the modern toy graph 上执行此遍历会产生以下结果:
gremlin> g = TinkerFactory.createModern().traversal()
==>graphtraversalsource[tinkergraph[vertices:6 edges:6], standard]
gremlin> g.V().match(
......1> __.as('v1').out().dedup().fold().as('v1n'),
......2> __.as('v1').V().as('v2'),
......3> __.as('v2').out().dedup().fold().as('v2n')).
......4> where('v1', lt('v2')).
......5> by(id).
......6> where('v1', without('v2n')).
......7> where('v2', without('v1n')).as('m').
......8> project('v1','v2','i','u').
......9> by(select('v1')).
.....10> by(select('v2')).
.....11> by(select('v1n').as('n').
.....12> select('m').
.....13> select('v2n').unfold().
.....14> where(within('n')).
.....15> count()).
.....16> by(union(select('v1n'),
.....17> select('v2n')).unfold().
.....18> dedup().count()).
.....19> filter(select('u').is(gt(0))).
.....20> project('v1','v2','j').
.....21> by(select('v1')).
.....22> by(select('v2')).
.....23> by(math('i/u'))
==>[v1:v[1],v2:v[5],j:0.0]
==>[v1:v[1],v2:v[6],j:0.3333333333333333]
==>[v1:v[2],v2:v[4],j:0.0]
==>[v1:v[2],v2:v[6],j:0.0]
==>[v1:v[4],v2:v[6],j:0.5]
==>[v1:v[5],v2:v[6],j:0.0]