手工计算对数
Calculate logarithm by hand
我想计算 mathematical logarithm "by hand"...
)
... 其中  代表 logarithmBase 和
代表 logarithmBase 和 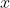 代表值。
代表值。
一些示例(参见Log calculator):
The base 2 logarithm of 10 is 3.3219280949
The base 5 logarithm of 15 is 1.6826061945
...
Hoever - 我不想使用像 Math.ceil, Math.log, Math.abs, ... 这样已经实现的函数调用,因为我想要一个干净的本机解决方案,它只处理 +-*/ 和一些循环。
这是我目前得到的代码:
function myLog(base, x) {
let result = 0;
do {
x /= base;
result ++;
} while (x >= base)
return result;
}
let x = 10,
base = 2;
let result = myLog(base, x)
console.log(result)
但上面的方法似乎不是计算以 N 为底的 对数的正确方法 - 因此,我们将不胜感激如何修复此代码的任何帮助。
提前一百万感谢乔纳斯。
您可以使用递归方法:
const log = (base, n, depth = 20, curr = 64, precision = curr / 2) =>
depth <= 0 || base ** curr === n
? curr
: log(base, n, depth - 1, base ** curr > n ? curr - precision : curr + precision, precision / 2);
可用作:
log(2, 4) // 2
log(2, 10) // 3.32196044921875
您可以通过更改 depth 来影响精度,您可以使用 curr
更改可接受值的范围(当前为 ~180)
工作原理:
如果我们已经达到了想要的深度或者如果我们已经找到了一个准确的值:
depth <= 0 || base ** curr === n
然后 returns curr 就完成了。否则它会检查我们要查找的对数是否低于或高于当前的对数:
base ** curr > n
然后它将继续递归地搜索一个值
1) 将 depth 降低一
2) 按当前精度增加/减少curr
3) 较低的精度
如果你讨厌函数式编程,这里有一个命令式版本:
function log(base, n, depth = 20) {
let curr = 64, precision = curr / 2;
while(depth-- > 0 && base ** curr !== n) {
if(base ** curr > n) {
curr -= precision;
} else {
curr += precision;
}
precision /= 2;
}
return curr;
}
对了,我用的算法叫"logarithmic search"俗称"binary search"。
第一种方法:使用 table 个常量。
首先将参数标准化为 1 到 2 之间的数字(这是通过根据需要多次乘以或除以 2 来实现的 - 记录这些操作的数量)。为了提高效率,如果值可以跨越多个数量级,您可以使用平方序列 2、4、16、256... 代替相等因子,然后在将值括起来时进行二分法搜索。
F.i。如果指数 16=2^4 有效但 256=2^8 无效,您尝试 2^6,然后根据结果尝试 2^5 和 2^7 之一。如果最终指数为 2^d,则线性搜索需要 O(d) 操作,而 geometric/dichotomic 仅搜索 O(log d)。为避免分裂,建议保留 table 个负幂。
归一化后,需要细化尾数。将该值与√2比较,如果较大则乘以1/√2。这使值介于 1 和 √2 之间。然后比较√√2等等。随着您的进行,当比较 returns 更大时,您将权重 1/2、1/4... 添加到指数。
最后的指数是以2为底的对数
示例:lg 27
27 = 2^4 x 1.6875
1.6875 > √2 = 1.4142 ==> 27 = 2^4.5 x 1.1933
1.1933 > √√2 = 1.1892 ==> 27 = 2^4.75 x 1.0034
1.0034 < √√√2 = 1.0905 ==> 27 = 2^4.75 x 1.0034
...
真实值为 4.7549。
请注意,您可以使用其他碱基,尤其是 e。在某些情况下,base 2 允许使用快捷方式,这就是我使用它的原因。当然,平方根要制表。
第二种方法:用泰勒级数
归一化步骤后,可以使用标准系列
log(1 + x) = x - x²/2 + x³/3 - ...
收敛于 |x| < 1。 (注意:我们现在有自然对数。)
由于接近1的值收敛太慢,建议使用上述方法缩小到[1,√2)范围内。然后每个新术语都会带来新的准确性。
或者,您可以使用 log((1 + x)/(1 - x)) 的级数,即使对于参数 2,它也能提供良好的收敛速度。参见 https://fr.wikipedia.org/wiki/Logarithme_naturel#D%C3%A9veloppement_en_s%C3%A9rie
示例:x = 1.6875,y = 0.2558 和
2 x (0.2558 + 0.2558³/3 + 0.2558^5/5) = 0.5232
lg 27 ~ 4 + 0.5232 / ln 2 = 4.7548
我想计算 mathematical logarithm "by hand"...
... 其中 代表 logarithmBase 和
代表值。
一些示例(参见Log calculator):
The base 2 logarithm of 10 is 3.3219280949
The base 5 logarithm of 15 is 1.6826061945
...
Hoever - 我不想使用像 Math.ceil, Math.log, Math.abs, ... 这样已经实现的函数调用,因为我想要一个干净的本机解决方案,它只处理 +-*/ 和一些循环。
这是我目前得到的代码:
function myLog(base, x) {
let result = 0;
do {
x /= base;
result ++;
} while (x >= base)
return result;
}
let x = 10,
base = 2;
let result = myLog(base, x)
console.log(result)
但上面的方法似乎不是计算以 N 为底的 对数的正确方法 - 因此,我们将不胜感激如何修复此代码的任何帮助。
提前一百万感谢乔纳斯。
您可以使用递归方法:
const log = (base, n, depth = 20, curr = 64, precision = curr / 2) =>
depth <= 0 || base ** curr === n
? curr
: log(base, n, depth - 1, base ** curr > n ? curr - precision : curr + precision, precision / 2);
可用作:
log(2, 4) // 2
log(2, 10) // 3.32196044921875
您可以通过更改 depth 来影响精度,您可以使用 curr
工作原理:
如果我们已经达到了想要的深度或者如果我们已经找到了一个准确的值:
depth <= 0 || base ** curr === n
然后 returns curr 就完成了。否则它会检查我们要查找的对数是否低于或高于当前的对数:
base ** curr > n
然后它将继续递归地搜索一个值
1) 将 depth 降低一
2) 按当前精度增加/减少curr
3) 较低的精度
如果你讨厌函数式编程,这里有一个命令式版本:
function log(base, n, depth = 20) {
let curr = 64, precision = curr / 2;
while(depth-- > 0 && base ** curr !== n) {
if(base ** curr > n) {
curr -= precision;
} else {
curr += precision;
}
precision /= 2;
}
return curr;
}
对了,我用的算法叫"logarithmic search"俗称"binary search"。
第一种方法:使用 table 个常量。
首先将参数标准化为 1 到 2 之间的数字(这是通过根据需要多次乘以或除以 2 来实现的 - 记录这些操作的数量)。为了提高效率,如果值可以跨越多个数量级,您可以使用平方序列 2、4、16、256... 代替相等因子,然后在将值括起来时进行二分法搜索。
F.i。如果指数 16=2^4 有效但 256=2^8 无效,您尝试 2^6,然后根据结果尝试 2^5 和 2^7 之一。如果最终指数为 2^d,则线性搜索需要 O(d) 操作,而 geometric/dichotomic 仅搜索 O(log d)。为避免分裂,建议保留 table 个负幂。
归一化后,需要细化尾数。将该值与√2比较,如果较大则乘以1/√2。这使值介于 1 和 √2 之间。然后比较√√2等等。随着您的进行,当比较 returns 更大时,您将权重 1/2、1/4... 添加到指数。
最后的指数是以2为底的对数
示例:lg 27
27 = 2^4 x 1.6875
1.6875 > √2 = 1.4142 ==> 27 = 2^4.5 x 1.1933
1.1933 > √√2 = 1.1892 ==> 27 = 2^4.75 x 1.0034
1.0034 < √√√2 = 1.0905 ==> 27 = 2^4.75 x 1.0034
...
真实值为 4.7549。
请注意,您可以使用其他碱基,尤其是 e。在某些情况下,base 2 允许使用快捷方式,这就是我使用它的原因。当然,平方根要制表。
第二种方法:用泰勒级数
归一化步骤后,可以使用标准系列
log(1 + x) = x - x²/2 + x³/3 - ...
收敛于 |x| < 1。 (注意:我们现在有自然对数。)
由于接近1的值收敛太慢,建议使用上述方法缩小到[1,√2)范围内。然后每个新术语都会带来新的准确性。
或者,您可以使用 log((1 + x)/(1 - x)) 的级数,即使对于参数 2,它也能提供良好的收敛速度。参见 https://fr.wikipedia.org/wiki/Logarithme_naturel#D%C3%A9veloppement_en_s%C3%A9rie
示例:x = 1.6875,y = 0.2558 和
2 x (0.2558 + 0.2558³/3 + 0.2558^5/5) = 0.5232
lg 27 ~ 4 + 0.5232 / ln 2 = 4.7548